About Recurrent Neural Network
-
RNN和普通的神经网络的区别在于,它中间隐层的状态不仅取决于输入值,还取决于隐层之前的状态值。即对于普通的神经网络,
S = f(W * X + b),其中S为隐层的状态值(可以理解为隐层神经元的输出),X为输入向量,W为隐层神经元的权重,b为偏置,f为激活函数;而对于RNN,S1 = f(W * X + b + W_s * S0),其中,S1为隐层当前的状态值,S0为隐层上一个时刻的状态值,W_s为权重。RNNs are called recurrent because they perform the same task for every element of a sequence, with the output being depended on the previous computations.
-
因为RNN隐层上一时刻的状态值又包含了上上一时刻的状态值,所以理论上,某一时刻隐层的状态值是有其之前的所有时刻的状态值共同决定的。假设W_s是小于1的权重,那么越靠近当前时刻的状态对目前状态的影响越大,这也比较符合我们的经验认知。
In theory RNNs can make use of information in arbitrarily long sequences, but in practice they are limited to looking back only a few steps (more on this later).
-
如果我们把RNN中循环的网络展开来,其实很像含有多个隐层的普通神经网络,只不过每个隐层都多了一个外部输入,且所有隐层共享了权重和偏置(这一点不禁联想到CNN)。在某种程度上来说,RNN和CNN都可以算是DNN的特例,所以也不要奇怪有些事情不光CNN能做,RNN也能实现(甚至DNN也可以做到)。比如说这个代码就实现了使用RNN来对MNIST手写数字进行分类,它把图像的每一行像素作为输入,输入到一个循环了N(N为图像高度)次的RNN中,最后用一个全连接层作为输出。
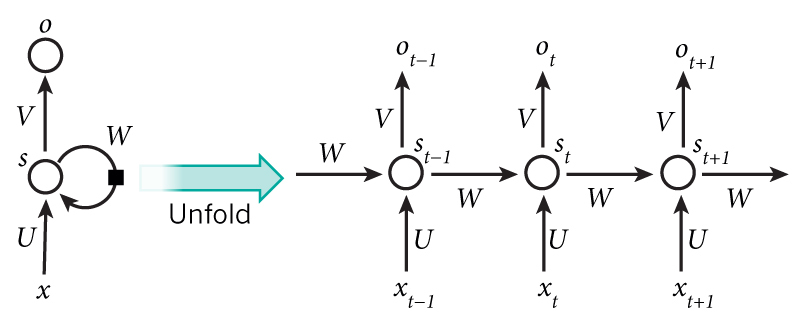
-
RNN的网络结构有这么几种:
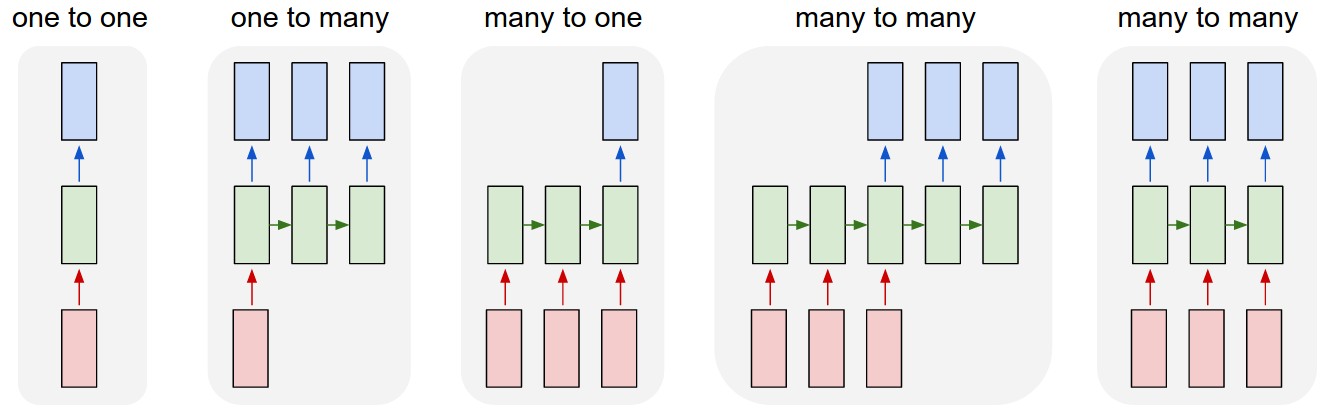
Each rectangle is a vector and arrows represent functions (e.g. matrix multiply). Input vectors are in red, output vectors are in blue and green vectors hold the RNN’s state (more on this soon). From left to right: (1) Vanilla mode of processing without RNN, from fixed-sized input to fixed-sized output (e.g. image classification). (2) Sequence output (e.g. image captioning takes an image and outputs a sentence of words). (3) Sequence input (e.g. sentiment analysis where a given sentence is classified as expressing positive or negative sentiment). (4) Sequence input and sequence output (e.g. Machine Translation: an RNN reads a sentence in English and then outputs a sentence in French). (5) Synced sequence input and output (e.g. video classification where we wish to label each frame of the video). Notice that in every case are no pre-specified constraints on the lengths sequences because the recurrent transformation (green) is fixed and can be applied as many times as we like.
-
How to predict the 10th value if we set the length of recurrent steps to 100?
根据下面的条目9可知,一种思路是一次性直接输出所有step的预测值,当然计算损失时也要把所有step都考虑进去。
-
How to predict only one output if we use the batch more than 1 for training?
要知道我们训练的是神经网络的参数,这些参数的维度和数目是和batch的size无关的,它们取决于输入向量的维度、神经元的数目等。因此,对于神经网络,我们给定输入的batch size,那么输出也是同样的batch size,即使在训练过程中,它(理论上)也完全是可以变化的,batch的作用仅仅在于计算损失时可以同时考虑多个样本而已。
之所以有这个问题是因为在使用tensorflow时碰到了输入的size不匹配会报错的情况,因为tensorflow中一个model一旦定义好就是固定的了。解决方法是定义模型是不要写死batch size那个维度,或者把训练的模型(即模型的参数)保存下来,预测时重新定义一个模型并加载训练好的模型:
sess = tf.Session() saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables()) saver.restore(sess, 'model/model') # Load trained model -
LSTM and GRU
两者都是RNN cell的特殊实现,主要目的是为了克服步数很多时训练时梯度弥散的问题(DNN深度很深时也存在类似的问题,之前提到过用batch normalization来克服这一问题)。
-
How to form multi-layer RNN cells?
这里的RNN cell就是RNN网络中的一层,原理上来说很简单,和普通的NN类似,后一层的输入即为前面一层的输出以及自己上一次的状态。
而在tensorflow中,它已经帮我们封装好了这些内部的东西,我们不需要用一个for循环来把上一层的输出和上一次的状态反复输入到RNN cell中,只需要定义网络的结构即可,比如下面定义了一个两层的RNN,且每层都进行了dropout(RNN的步数是由inputs的维数来确定的,最后的输出是包含了每一步的输出的一组向量):
rnn_cell1 = tf.nn.rnn_cell.GRUCell(num_units=64, activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu) cell1 = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(rnn_cell1, output_keep_prob=keep_prob) rnn_cell2 = tf.nn.rnn_cell.GRUCell(num_units=128, activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu) cell2 = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(rnn_cell2, output_keep_prob=keep_prob) multi_rnn_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([cell1, cell2]) # Initial state of the RNN memory. state = multi_rnn_cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32) rnn_outputs, final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn( multi_rnn_cell, inputs, initial_state=state, time_major=False, # False: (batch, time step, input); True: (time step, batch, input) ) -
How to connect RNN cell with full connected layer?
看了char-rnn项目,它是直接把RNN cell的输出作为全连接层的输入来训练的。这里RNN的输出包含了每一步(time step)的输出,以生成文字为例,假设文字类别为N,则使用一个含有N个神经元的全连接层;每一步,RNN的输出经过全连接层都可以得到一个预测的文字,最终可以得到一个长度为M的文字序列。
Reference
- http://www.wildml.com/2015/09/recurrent-neural-networks-tutorial-part-1-introduction-to-rnns/
- http://karpathy.github.io/2015/05/21/rnn-effectiveness/
- https://github.com/sherjilozair/char-rnn-tensorflow

Comments