关于Python标准库logging
-
logging这个类有点特别,它会在初始化时生成一个全局的对象用来存储所有logger对象,而后每次import logging,可以通过getlogger来获取特定的logger对象,从而打印出相应的log。所以它类似一个树状的结构,logging.INFO()其实就是root.INFO(),是直接用根节点来打log(根节点是在import logging时就会初始化);
-
logging的子节点如果没有setLevel的话,默认level为0,意思是一个无效的level,会通过如下方法来搜索其父节点,直到找到有效的level位置;
def getEffectiveLevel(self): """ Get the effective level for this logger. Loop through this logger and its parents in the logger hierarchy, looking for a non-zero logging level. Return the first one found. """ logger = self while logger: if logger.level: return logger.level logger = logger.parent return NOTSET -
logging的官方流程图:
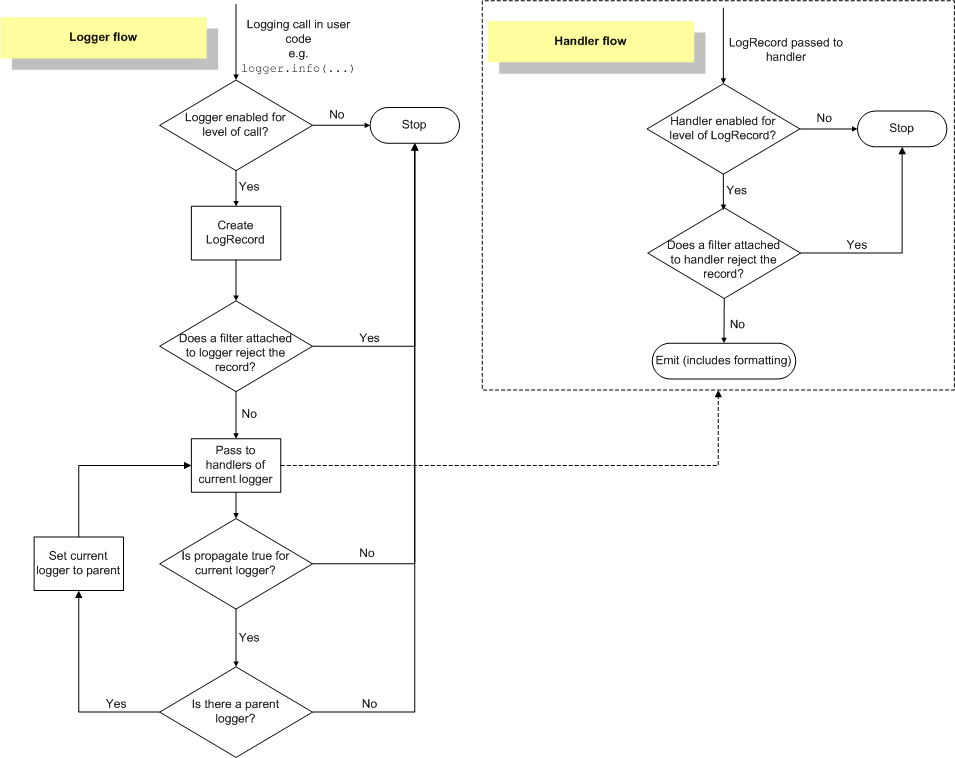
-
logging默认的root节点的level是WARNING:
root = RootLogger(WARNING) -
执行某个logger.info()时,默认会call这个logger以及它所有父节点的handler,如果不想call其父节点的handler,则需要把logger.propagate设为False。这部分源代码如下:
def callHandlers(self, record): """ Pass a record to all relevant handlers. Loop through all handlers for this logger and its parents in the logger hierarchy. If no handler was found, output a one-off error message to sys.stderr. Stop searching up the hierarchy whenever a logger with the "propagate" attribute set to zero is found - that will be the last logger whose handlers are called. """ c = self found = 0 while c: for hdlr in c.handlers: found = found + 1 if record.levelno >= hdlr.level: hdlr.handle(record) if not c.propagate: c = None #break out else: c = c.parent if (found == 0) and raiseExceptions and not self.manager.emittedNoHandlerWarning: sys.stderr.write("No handlers could be found for logger" " \"%s\"\n" % self.name) self.manager.emittedNoHandlerWarning = 1 -
使用logging打印出exception的stack trace:
try: # do something here except Exception, e: logging.error(e, exc_info=True)
